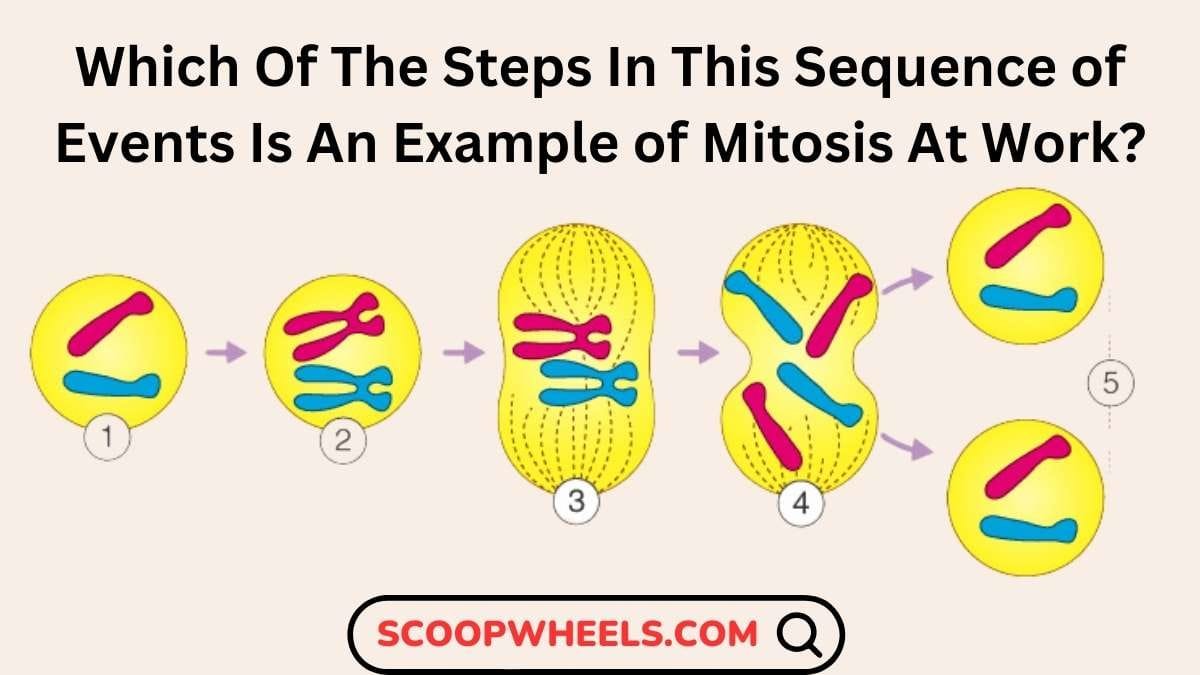
Like most biological processes, mitosis is a significant factor that is mainly involved in the division of one cell into two genetically similar daughter cells. This basic process is in all eukaryotic organisms where growth and tissue repair are asexual form of reproduction. Do you Know, which of the steps in this sequence of events is an example of mitosis at work? Let’s know the all the details through this article.
What is Mitosis?
Mitosis is a complex and closely organized process that occurs in eukaryotic cells wherein a single cell gives rise to two genetically identical daughter cells. Mitosis is important to guarantee that a potential daughter cell gets an interchange copy of the genetic makeup. This cycle takes place in the somatic cells that are the body cells that are not involved in the reproduction process. And it is useful in growth, repair as well as the multicellular creatures’ cell replacement.
Which of the steps in this sequence of events is an example of mitosis at work?
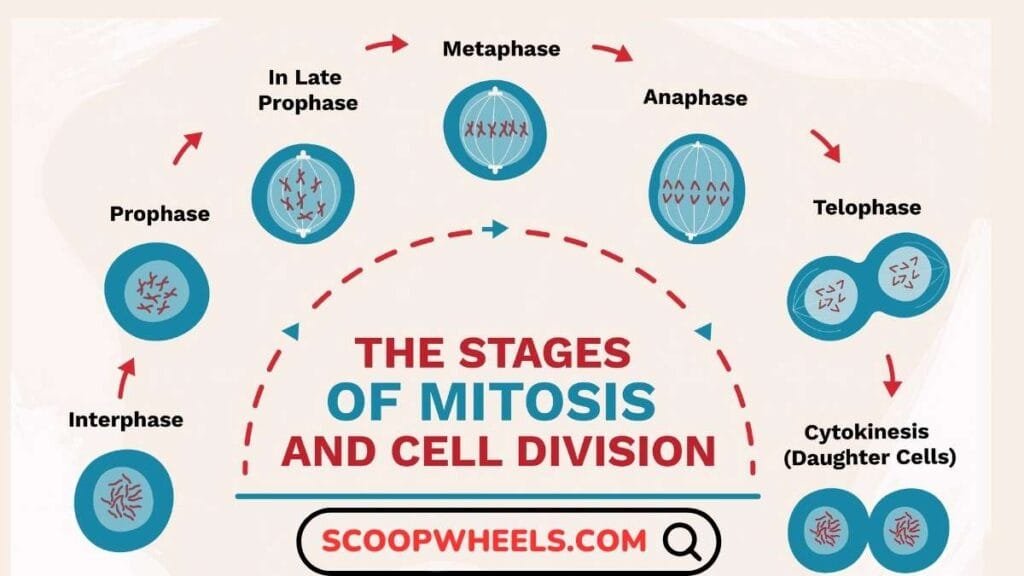
There are few steps in mitosis and every single step is important for the right division of the genetic material between two new cells. Let’s explore each stage in detail:
1. Prophase: Preparation for Division
Prophase is basically the first phase of mitosis and can be distinguished by the initiation of the spindle preparations and of the nuclear divisions.
- Chromatin Condensation: Chromatin a combination of DNA with proteins pulls back into tighter, more apparent structures called chromosomes. This step is crucial because during cell division, the chromosomes could be easily controlled by the mechanisms of the cell.
- Spindle Fiber Formation: During this stage the microtubules of the cell start to develop the mitotic spindle —– an organelle that is instrumental in the positioning of the chromosomes. Of these spindle fibers, some come from the centrosomes that are specific areas of the cell concerned with the arrangement of microtubules.
- Nuclear Envelope Breakdown: The nuclear membrane that surrounds the nucleus begins to disintegrate in order to let the mitotic spindle get to the chromosomes. This is important so as to facilitate direct access to the genetic material by the cellular structures.
2. Metaphase: Chromosome Alignment
In general, metaphase is the second phase of mitosis, during which the chromosomes are located on the equatorial plane of the cell. An organism couldn’t evolve, much alone repair itself or replace any damaged cells, if it couldn’t go through mitosis. The following are a few of the primary roles that mitosis plays in organisms:
- Chromosome Alignment: Both homologous chromosomes, made up of two similar chromatids, align also along the metaphase plate equatorially. The spindle fibres hook themselves on to the centromere in each and every chromosome thus anchoring the chromosomes.
- Checkpoint: The cell does have a checkpoint system so that all its chromosomes are connected to the spindle fibers. And will be in a proper position before proceeding with the next stage and an equal distribution of chromosomes to each daughter cell is important.
3. Anaphase: Chromatid Separation
Anaphase is the third phase in mitosis and characterizes the actual separation of two sister chromatids. During this stage:
- Chromatid Separation: The sister chromatids are pulled apart by the spindle fibers, moving toward opposite poles of the cell.
- Centromere Splitting: The centromere, the region where the two chromatids are connected, splits, allowing the chromatids to be separated and moved to opposite sides of the cell.
4. Telophase: Reformation of the Nucleus
Telophase is the final stage of mitosis, where the cell begins to reassemble after chromosome separation:
- Chromosomes Decondense: This allows the chromosomes which were initially easily distinguished as different structures return to their state of chromatin. This is an important stage in the development with the aim of preparing the cell for the ultimate stage in the process of cell division.
- Nuclear Envelope Reforms: Each pair of chromosomes is surrounded by a new nuclear membrane and what was once a single nucleus is now two nuclei within the same cell. This is almost the end of nuclear division.
5. Cytokinesis: Final Separation
Cytokinesis is not strictly speaking part of mitosis but is the last event that takes place in the cycle of cell division.
- Cytoplasm Division: In animal cells, the pinching in of the membrane is create by a contractile ring. In the middle of the cell dividing the cytoplasm into two different sections. In plant cells, the centrosomes start approaching, and a cell plate is formed and later on transformed into a new cell.
- Cytokinesis is important in making sure that each daughter cell will have its own organelle and complete set of cytoplasmic components. two nested daughter nuclei are produce after cytokinesis which are genetically identical to the parent cell.
Which of the steps in this sequence of events is an example of mitosis at work? In Organisms
This process plays a critical role for the normal functioning of multicellular organisms. Without the ability to undergo mitosis, an organism would not be able to develop, much less heal itself or replace any damaged cells. Some of the main functions of mitosis in organisms include the following:
The following are some of the primary roles of mitosis in organisms:
- Growth and Development: As an organism develops it’s tissues, its cells multiply through the process of mitosis to make new cells.
- Tissue Repair: When it is cut or any type of injury occurs on certain tissues then mitosis aids in strength or rebuilding of some other such cells. This process is essential in the repairing and ultimately the healing of tissue.
- Asexual Reproduction: In most of the species, mitosis is the process employee for asexual reproduction. Mitosis also plays a significant role in single-celled organisms such as bacteria through which the offspring arise from the parent cell having the same genetic makeup.
Abnormalities in Mitosis and Their Consequences
It is regularly a highly control process, yet, errors might be produce. The failure in the processes of mitosis would result in the general effects with probably the most immense impact being cancerous cell production. Tumour cells divide uncontrollably because they have acquired abnormal versions of genes that control cell division and mitosis. They may cause aneuploidy, a condition where a cell has an abnormal number of chromosomes, or result in tumors beginning to increase out of control.
Conclusion
In this which of the steps in this sequence of events is an example of mitosis at work? Mitosis is in fact an intricate and delicately calibrated procedure without which growth and development of any living organism is inconceivable. The five stages of mitosis – prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase and cytokinesis guarantees that the hereditary blueprint of chromosomes is divided equally among both daughter cells. Thus, knowing the stages and the processes occurring during mitosis allows one to realize its significance in the context of life processes and the ability to restore and maintain the function of tissues and organs.
FAQ’s About Which of the steps in this sequence of events is an example of mitosis at work?
Ans. The main stages of mitosis are Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, and Cytokinesis.
Ans. During prophase, the chromatin condenses into chromosomes, and the nuclear envelope begins to break down while spindle fibers form.
Ans. Mitosis is essential for growth, tissue repair, and asexual reproduction, allowing organisms to produce new cells.
Ans. Errors in mitosis can lead to conditions like cancer or genetic disorders due to improper chromosome distribution.
Also Read About